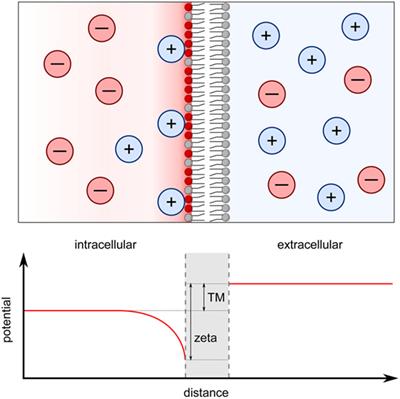
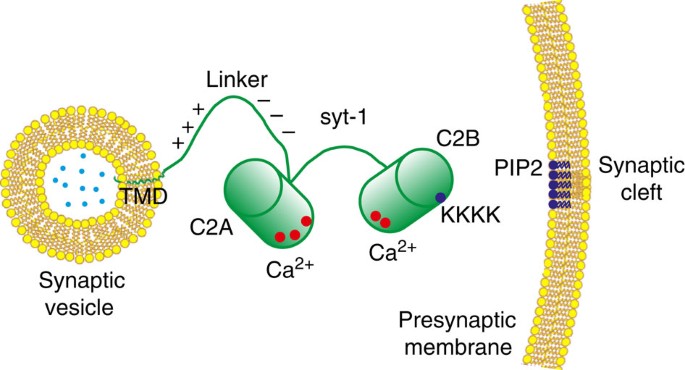
Particle Deformability Enables Control of Interactions between Membrane-Anchored Nanoparticles
€ 16.00 · 4.7 (707) · Auf Lager


Preferential binding of positive nanoparticles on cell membranes is due to electrostatic interactions: A too simplistic explanation that does not take into account the nanoparticle protein corona - ScienceDirect
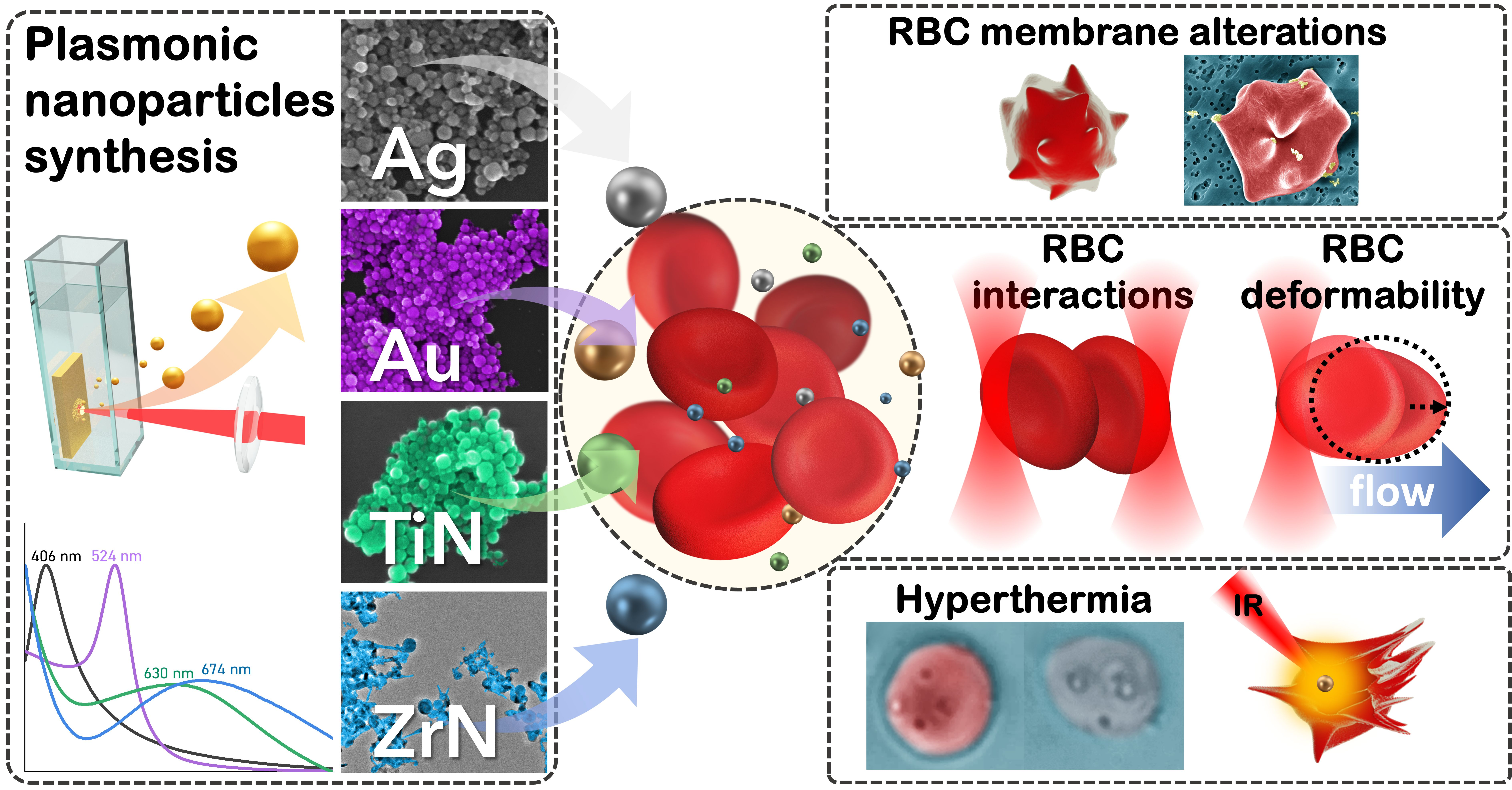
Pharmaceutics, Free Full-Text

Nanoparticles Meet Cell Membranes: Probing Nonspecific Interactions using Model Membranes
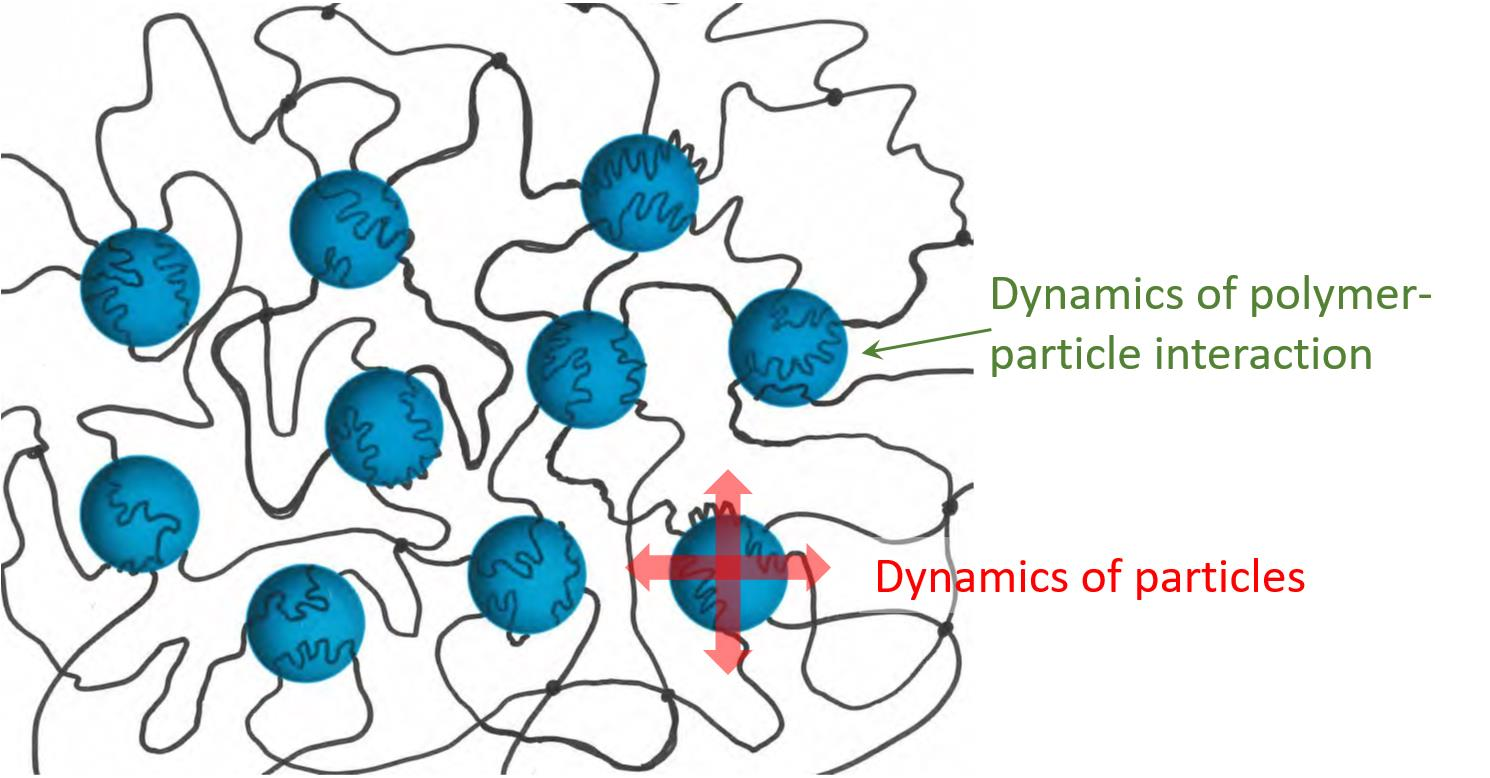
Polymers, Free Full-Text
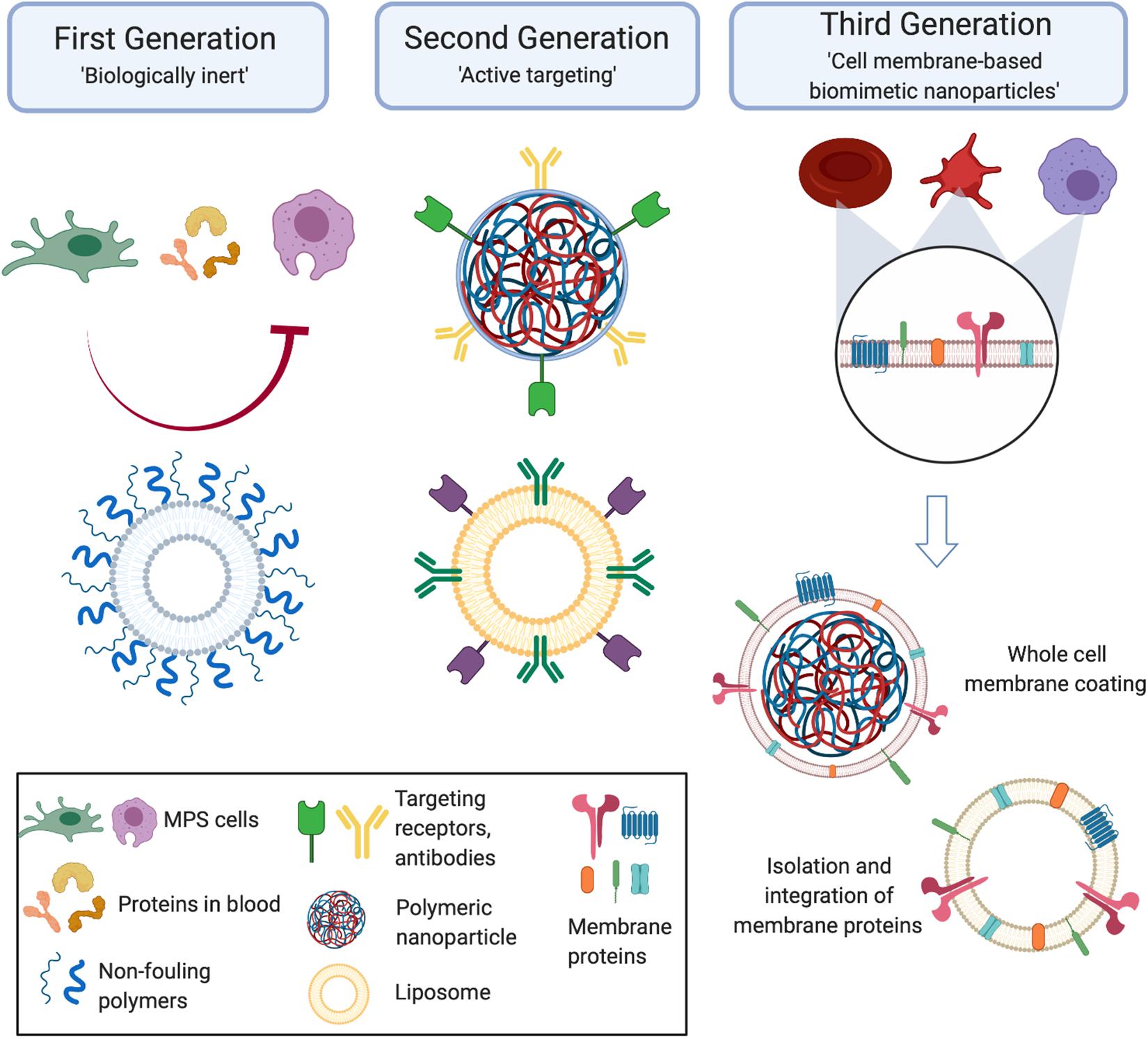
Frontiers Cell Membrane-Based Biomimetic Nanoparticles and the Immune System: Immunomodulatory Interactions to Therapeutic Applications

Cell-bound nanoparticles for tissue targeting and immunotherapy: Engineering of the particle–membrane interface - ScienceDirect

Cell Membrane-Camouflaged Nanocarriers with Biomimetic Deformability of Erythrocytes for Ultralong Circulation and Enhanced Cancer Therapy

Simulation of nanoparticles interacting with a cell membrane: probing the structural basis and potential biomedical application

Particle Deformability Enables Control of Interactions between Membrane-Anchored Nanoparticles

Nanoparticle-cell interactions: a reductive theory - Materials Today

Nanoparticle - Wikipedia

Biosafety of mesoporous silica nanoparticles; towards clinical translation - ScienceDirect

Simulation of nanoparticles interacting with a cell membrane: probing the structural basis and potential biomedical application
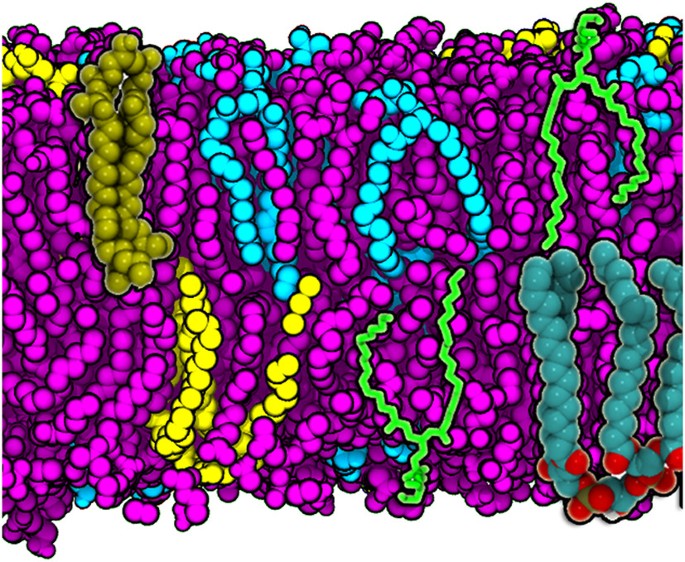
Understanding Conformational Dynamics of Complex Lipid Mixtures Relevant to Biology